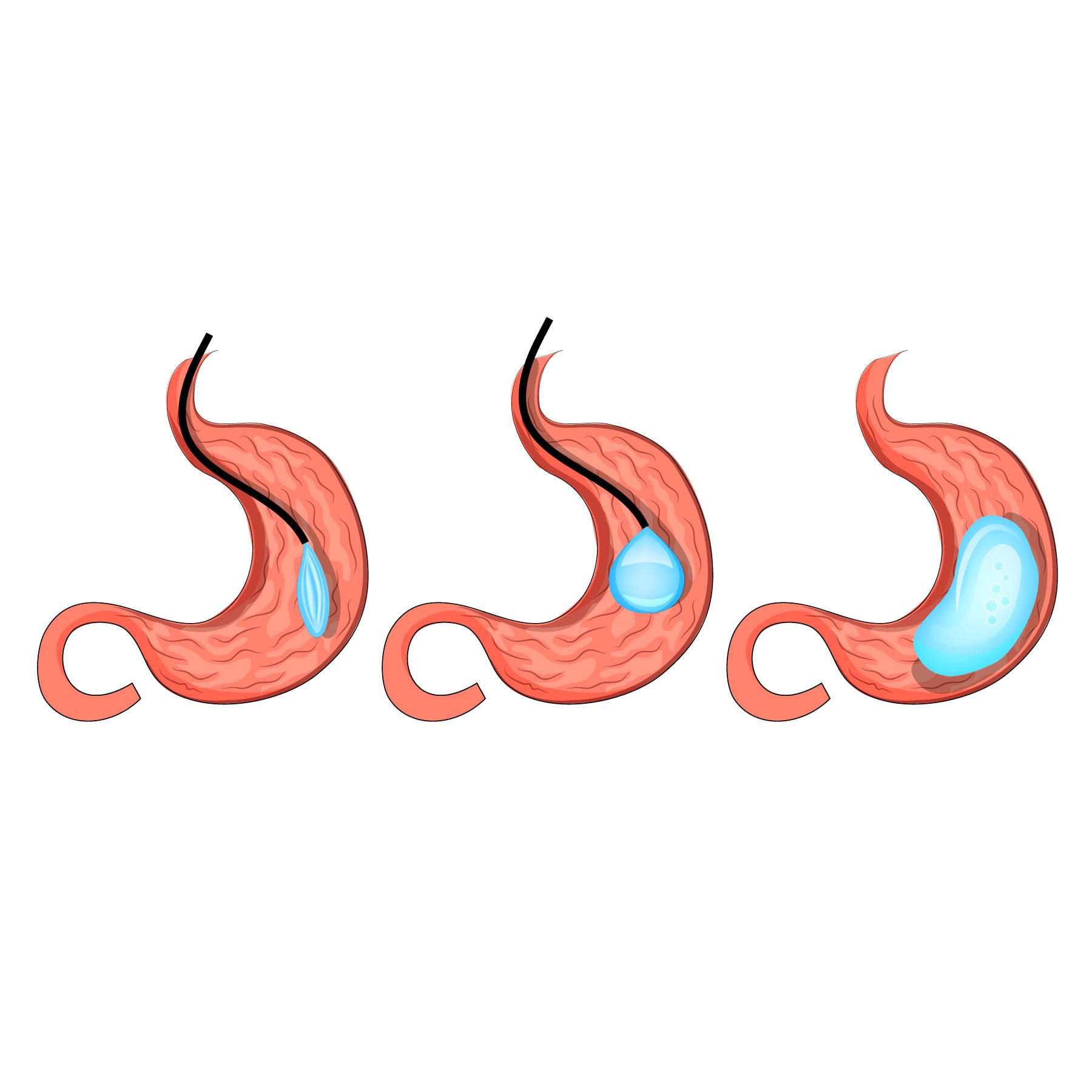
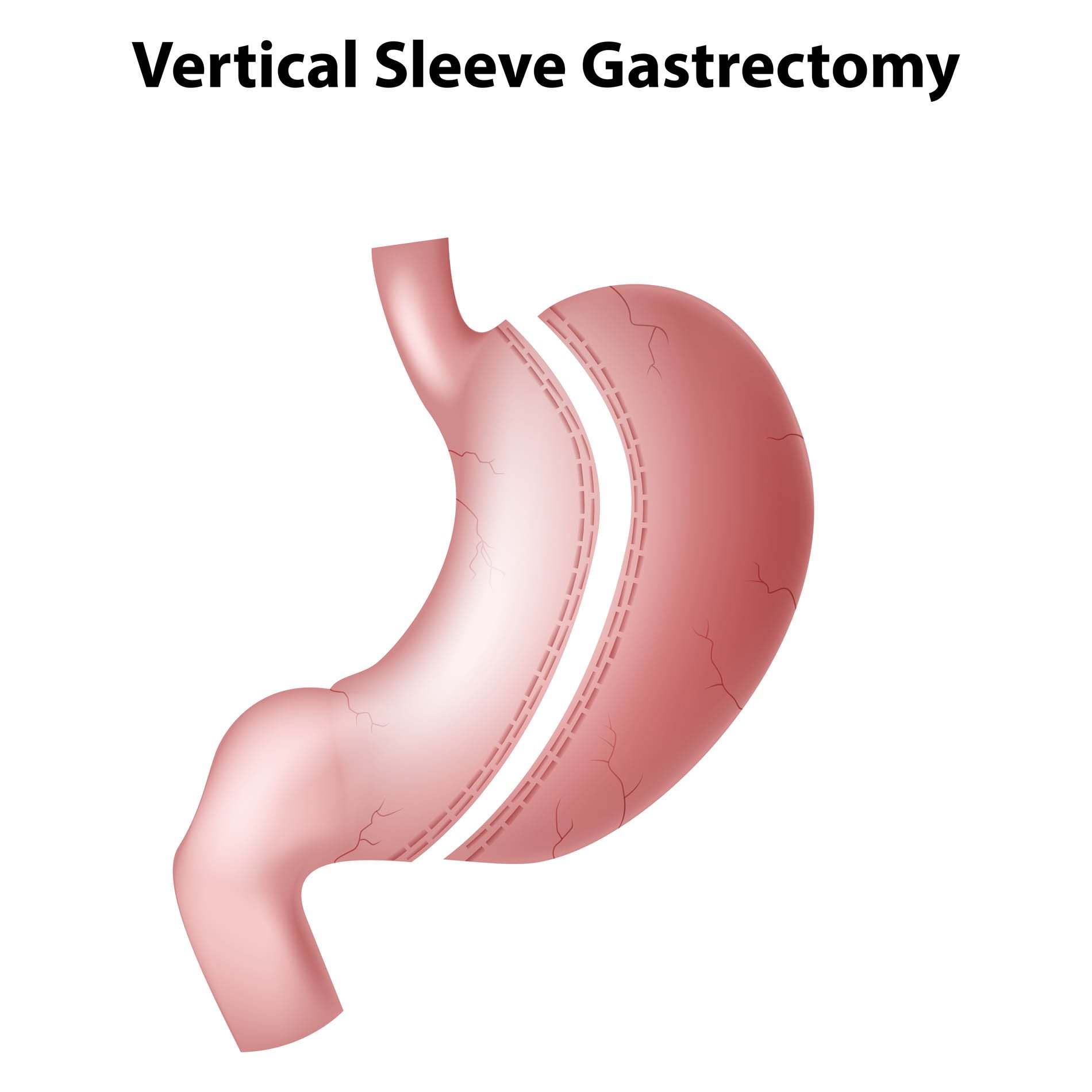
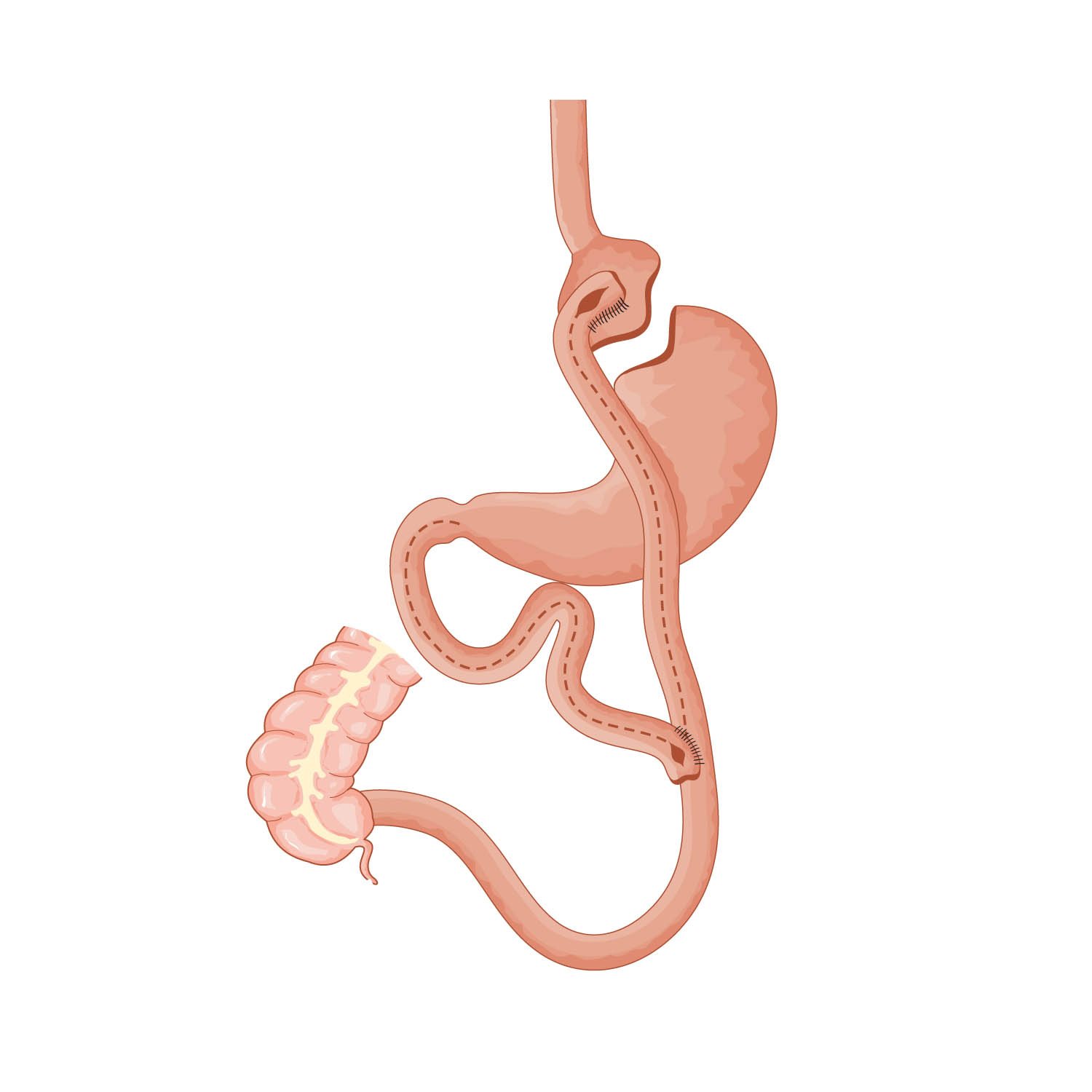
Obesity & Metabolic Surgery
Obesity is simply defined by the body having excessive fat. This excess fat has been found to be physiologically “active” & “harmful” and causes many systemic effects that will eventually lead to shortened survival of the individual. Metabolic surgery (MS) is the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity using a surgical method. The classical treatment paradigm of type 2 diabetes is education, exercise, diet and medications. However in some patients disease progression is inevitable despite best medical treatments. In such cases, metabolic surgery should be considered as a treatment alternative as studies have shown that established surgical procedures are associated with larger and more sustained weight loss and better obesity-related comorbidity outcomes (including diabetes remission) as compared to non-surgical interventions. In addition, recent studies already found that metabolic surgery has a positive impact on obstructive sleep apnea and the prevention of cancer.
The International Federation for the Surgery of Obesity and Metabolic Disorders (IFSO) has produced specific guidelines for Asian in 2011.
According to the IFSO- Asia Pacific Consensus 2011:
Bariatric surgery should be considered for the treatment of obesity for acceptable Asian candidates with BMI ≥ 35 with or without co-morbidities
Bariatric/GI metabolic surgery should be considered for the treatment of T2DM or metabolic syndrome for patients who are inadequately controlled by lifestyle alternations and medical treatment for acceptable Asian candidates with BMI ≥ 30
The surgical approach may be considered as a non-primary alternative to treat inadequately controlled T2DM, or metabolic syndrome, for suitable Asian candidates with BMI ≥ 27.5.